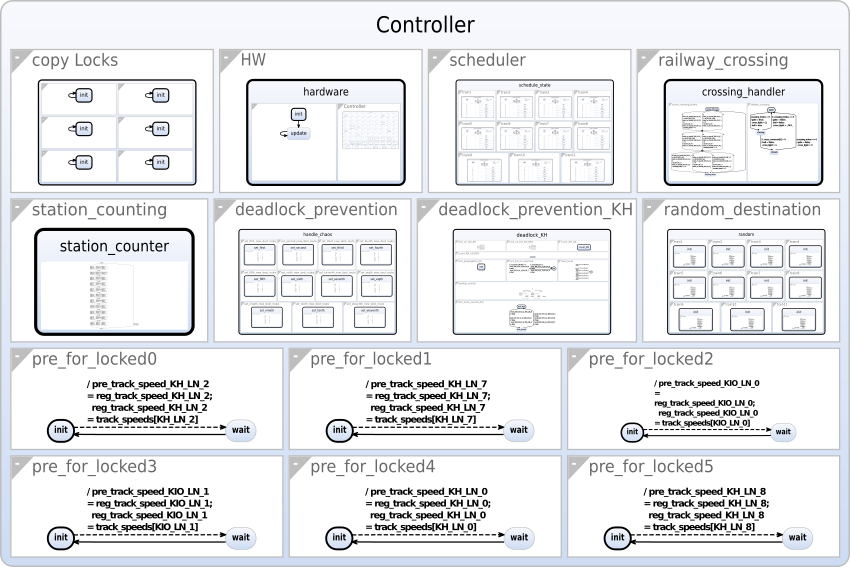
Top-down Layout is a technique to draw large hierarchical diagrams from the root node downwards, scaling children down to fit in the space provided by their parents. This is in contrast to bottom-up layout where children are laid out first and the parents' dimensions are determined accordingly afterwards.
In top-down layout a strategy needs to be used to set node sizes without knowledge of the hierarchical contents of the node as that has not been processed/laid out at that point. Current strategies are:
- using Using a default base size
- counting Counting the number of children and taking the square root as a multiplication factor for the default base size
- computing Computing the layout of only the children (look-ahead layout)
The main challenge is to get an approximation that gives a suitable aspect ratio (close to what will actually be required).
Because graphs Graphs are complex feature vectors and the solution space is very large without necessarily one correct and optimal answer. Therefore, a machine learning (ML)-based approach may help find good solutions.
This topic will be supervised in cooperation with the Intelligent Systems group.
Goals
...
Example Top-down Layout of an SCChart
Goals
- Use the KiCoDia benchmarking tool to extract feature vectors from existing models
- train Train and evaluate an ML model on the extracted data sets
- integrate Integrate the model as a new node size approximator into top-down layout
Example Top-down Layout of an SCChart
Scope
BachelorMaster's /Master(Bachelor's) Thesis
Related Work/Literature
[WIP] Under Review] M. Kasperowski and R. von Hanxleden, Top-down layout paperLayout: Effectively Utilizing Zoom for Drawings of Compound Graphs
M. Nielsen, Neural Networks and Deep Learning, Determination Press, 2015 (http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/index.html)
I. Goodfellow and Y. Bengio and A. Courville, Deep Learning, MIT Press, 2016 (https://www.deeplearningbook.org/)
Involved Languages/Technologies
- Java / Xtend, Python
- KiCo
- ML Frameworks (to be chosen)
Supervised by
Maximilian Kasperowski in cooperation with the Intelligent Systems group.
mka@informatik.uni-kiel.de