Page History
This page documents how KLay Layered implements label placement, port placement, and node sizing.
| Note | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Everything on this page is still subject to change – this is the bleeding edge of science! We're still working on this stuff, trying out different concepts, and moving things around, all for the benefit of mankind. You're welcome. |
Contents
| Table of Contents |
|---|
...
At first glance, label placement and node sizing are two separate problems. However, out of the three types of labels we currently support, two have considerable influence on the size of nodes (node labels and port labels, but you already figured this out yourself). Well, in fact, that's not completely true. It's not the labels that influence the size of nodes, it's the placement of labels. And if we didn't care for readability, the placement wouldn't influence node size at all. But we do. Take this simple example:
...
| title | ToDo |
|---|
...
The two nodes have two labeled labelled ports each. Let's assume port positions to be fixed, and labels to be placed inside the nodes. Clearly, the left node is While the port labels fit perfectly fine into Node 1, Node 2 is clearly too narrow for the port labels them to be placed without overlaps. If the labels are to be placed without overlaps, we need : we would have to increase the width of the node. Label placement influences node sizing.
Matters get more complicated if we allow port positions to be changed. If the western port is moved upwards and the eastern port downwards, the labels don't overlap anymoreany more. Thus, label placement also influences port placement.
...
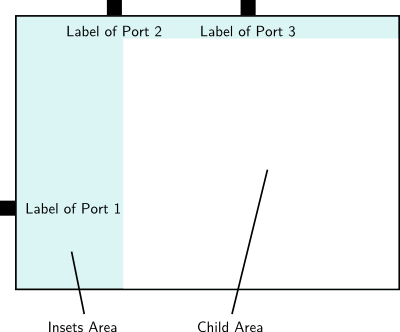
When it comes to label placement and node size calculations, we can think of a node as having the following anatomy:
The insets area is used as follows:
- If port labels are placed inside a node, the insets area is used to place them.
- If node labels are placed inside a node at one of the four sides (as apposed to centered), the insets area is used to place them.
the part of the node where port and node labels are placed (if they are placed inside the node as opposed to outside the node). The child area is what is left of the node with the insets subtracted. With the SizeConstraintSizeOptions.CHILDCOMPUTE_AREAINSETS, KLay Layered can compute the child area and return it. This makes it easy to use in cases where the child area of the node is going to be used for displaying graphics or further text. If a minimum size is set on the node and the options SizeConstraint.MINIMUM_SIZE and SizeConstraintSizeOptions.MINIMUM_SIZE_ACCOUNTS_FOR_INSETS are set, the minimum size will effectively only apply to the child area. Thus, KLay Layered can be told to ensure that the child area of a node has at least a certain given size, whatever space the port labels and node labels require.
...
- More than one port label. Who would want to have more than one anyway?More than one node label. More than one label can usually be combined into a single
KLabelobject if the relative locations of the labels don't change - Different placements for each node label. As of now, node labels are placed by arranging them in a vertical stack at the desired node label position.
General Approach
The general approach to solving label placement, port placement, and node sizing follows the following general pattern:
- Place port labels
- Place ports
- Reserve space for node labels
- Resize nodeCalculate required insets
- Resize node
- Place ports
- Place node labels
- Calculate insets
Each task will be described in more detail in the following.
...
Each port's labels are placed. The exact placement strategy may differ depending on node sizing and port placement constraints. The easiest way of placing port labels, however, is not to care about other constraints just yet.
Place Ports
All ports are placed. If node sizing constraints allow for it, ports are placed in a way that ensures that port labels don't overlap each other. This is only possible, though, if SizeConstraint.PORT_LABELS is set. In all other cases, we can only hope that the result is free of overlaps.
This step also computes the insets of the node.
Reserve Space for Node Labels
...
Calculate Required Insets
Before resizing the node, we will need to find out how large it will have to be at the minimum. This requires iterating over ports and labels to find out how much space they will need, which is what this step is all about.
Resize Node
With the insets calculated, this step resizes the node, ensuring that the node size constraints are met. If the node is to have a minimum size, it may be resized accordingly, for instance. If ports are to be taken into account for the size calculation, the node size is adjusted to accommodate for its ports.
Place
...
Once the node size is calculated, node labels are placed.
Port Placement
Ports
All ports are placed. If node sizing constraints allow for it, ports are placed in a way that ensures that port labels don't overlap each other. This is only possible, though, if SizeConstraint.PORT_LABELSis set. In all other cases, we can only hope that the result is free of overlaps.
The only cases where we even have to talk about the placement of ports are those where their position is not fixed. That more or less leaves us with the three port constraints FREE, FIXED_SIDES, and FIXED_ORDER. The first is reduced to the second by assigning ports to the eastern or western side depending on the number of incoming and outgoing edges (if a port has more outgoing edges than incoming ones, it can be regarded as an output port). The second is reduced to the third during crossing minimization, in an attempt to find an order that will yield the fewest amount of edge crossings. Thus, the only case of real interest to us is FIXED_ORDER.
...
- Label Placement: Ports should be placed in a way that avoids label overlaps.
- Node Sizing: If node sizing doesn't pay any attention to ports, port placement options may be severely restricted.
Place Node Labels
With the node size set and ports placed, the node labels are now placed.
Layout Options Influencing This Stuff
The following layout options influence how the algorithm places ports and labels and calculates the node size:
| Option | Target | Description |
|---|---|---|
LayoutOptions.NODE_LABEL_PLACEMENT | Node | Determines where node labels are placed. A valid set of values contains exactly one constant from each of the following sets of constants:
|
LayoutOptions.PORT_LABEL_PLACEMENT | Node | Determines where port labels are placed: inside or outside their node. |
LayoutOptions.LABEL_SPACING | Graph | Determines the amount of space left between labels and the objects they label. |
LayoutOptions.SIZE_CONSTRAINT | Node | The amount of freedom in determining the size of a node. |
LayoutOptions.SIZE_OPTIONS | Node | Options for node size calculation. |
LayoutOptions.MIN_WIDTH | Node | The minimal width of a node. If set, overrides the default minimal width. |
LayoutOptions.MIN_HEIGHT | Node | The minimal height of a node. If set, overrides the default minimal height. |
LayoutOptions.PORT_CONSTRAINTS | Node | Freedom in placing ports. |
Properties.PORT_SPACING | Node | How much space should be left between ports. |