Page History
KTM - KIELER Transformation Mapping
...
| Panel | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
This article is deprecated. The described features are no longer available in current releases. KTM was redesigned is now available as KiTT included in KiCool. |
Topics
| Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Transformation Tree Model
...
To offer a mapping between model-elements during multiple transformations KTM introduces a model called TransformationTree to represent these relations.
...
First part (upper half) is a tree of transformations. Each ModelModelWrapper-class is a representation of a concrete model which is transformed. So models So ModelWrapper are nodes and ModelTransformations are edges. Thus the Model the ModelWrapper representing the rootinitial-source-model of a tree all transformation is also the root of a concrete TransformationTree-model.
Second part (lower half) is object-mapping. Instances of models contain EObjects as their elements, which are represented by ElementEObjectWrapper-class in TransformationTree this metamodel. The Elements The EObjectWrapper of two models are connected with ElementTransformationsEObjectTransformations-class to model express their origination relationship in corresponding model transformation.
An abstract example of an instance of this model:
...
- All references to EObjects in EObjectWrapper are references to a copy of the original EObject. This allows to represent immutable mapping. To reidentify corresponding EObjects TransformationTreeExtensions provides search functions which will check for structural matching models.
- Models in TransformationTrees may be transient. This indicates that all references to EObjects in all Elements of the transient model are removed. Thus these models can't be source of a new appended transformation and can not be associated with it's original model. The main propose of this feature is to improve scalability of TransformationTrees by removing unnecessary references to internal model, but preserve traversing functionality of the ObjectMappingobject-mapping.
- Mappings can be incomplete causing resulting transfromation tree to be incomplete. A incomplete tree does not represent every object in a model with a corresponding Element. This may break some paths of element transformations, but allows to omit model-immanent objects like annotations from mapping. TranformationMapping extension provies a function to check completeness of mapping against its models.
...
Example
Creating Mapping during Transformation
The following code is a modifcation of the tranformation "Spilt Trigger and Effects" of SCCharts.
...
In this example we will perform some transformations on SCCharts.
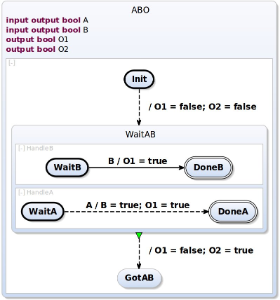
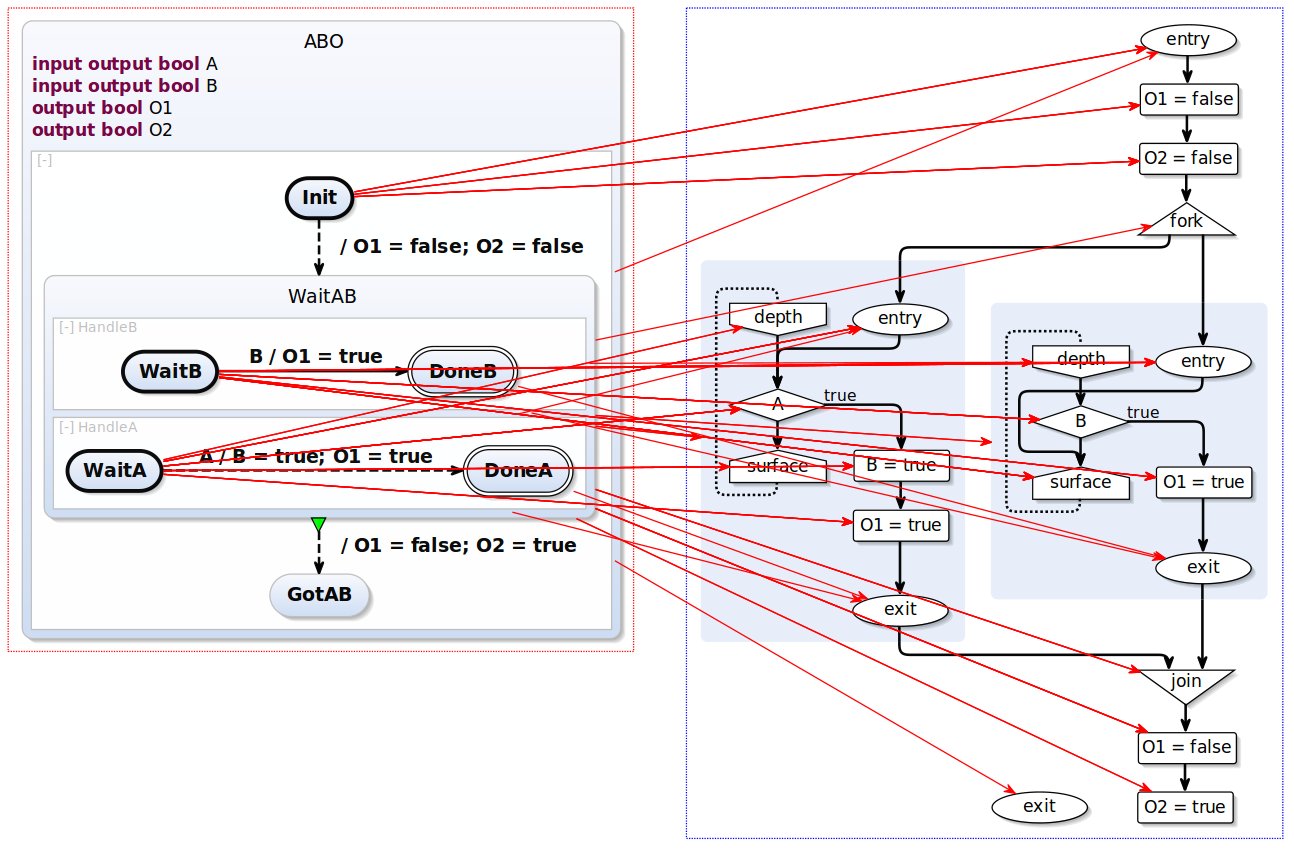
The source chart is a ABO, the "Hello World" of SCCharts.
ABO is already a CoreSCChart, so we will perform normalization and a transformation to SCG.
Creating Mapping during Transformation
In order to note every single element transformation of a model transformation, we use the TransformationMapping extension.
After each creation of new Objects for transformed model the mapping must be updated with it's origin information.
The codeblock blow show a snipped of SCChartCoreTransformation with additional mapping registration.
| Code Block | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||
package de.cau.cs.kieler.ktm.test.transformations import com.google.inject.Inject import de.cau.cs.kieler.ktm.extensions.TransformationMapping import de.cau.cs.kieler.sccharts.Region import de.cau.cs.kieler.sccharts.Transition import de.cau.cs.kieler.sccharts.extensions.SCChartsExtension /** * @author als */ class SCChartTestTransformation { @Inject @Inject extension TransformationMapping @Inject extension SCChartsExtension ... // NEW -- Mapping Accessaccess delegation def extractMapping() { extractMappingData; } ... //------------------------------------------------------------------------- //-- S P L I T T R A N S I T I O N -- //------------------------------------------------------------------------- // For every transition T that has both, a trigger and an effect do the following: // For every effect: // Create a conditional C and add it to the parent of T's source state S_src. // create a new true triggered immediate effect transition T_eff and move all effects of T to T_eff. // Set the T_eff to have T's target state. Set T to have the target C. // Add T_eff to C's outgoing transitions. def Region transformTriggerEffect(Region rootRegion) { clearMapping; //NEW - clear previous mapping information to assure a single consistent mapping // Clone the complete SCCharts region var targetRootRegion = rootRegion.mappedCopy; //NEW - mapping information (changed copy to mappedCopy) // Traverse all transitions for (targetTransition : targetRootRegion.getAllContainedTransitions) { targetTransition.transformTriggerEffect(targetRootRegion); } val completeness = checkMappingCompleteness(rootRegion, targetRootRegion); //NEW - DEBUG targetRootRegion; } def void transformTriggerEffect(Transition transition, Region targetRootRegion) { // Only apply this to transition that have both, a trigger (or is a termination) and one or more effects if (((transition.trigger != null || !transition.immediate || transition.typeTermination) && !transition.effects.nullOrEmpty) || transition.effects.size > 1) { val targetState = transition.targetState val parentRegion = targetState.parentRegion val transitionOriginalTarget = transition.targetState var Transition lastTransition = transition val firstEffect = transition.effects.head for (effect : transition.effects.immutableCopy) { // Optimization: Prevent transitions without a trigger if(transition.immediate && transition.trigger == null && firstEffect == effect) { // skip } else { val effectState = parentRegion.createState(targetState.idGENERATED_PREFIX + effect.id"S") effectState.mapParents(transition.mappedParents); //NEW - mapping information effectState.setTypeConnectoruniqueName val effectTransition = createImmediateTransition.addEffect(effect) effectTransition.mapParents(transition.mappedParents); //NEW - mapping information effectTransition.setSourceState(effectState) lastTransition.setTargetState(effectState) lastTransition = effectTransition } } lastTransition.setTargetState(transitionOriginalTarget) } } } |
Create TransformationTree
...
The following code snipped performs the transformation on our ABO-example, extracts the mapping and creates will now perform each transformation stepwise and updates a transformation tree each step.
| Code Block | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||
aboSplitTE = transformationSCCtransformation.transformTriggerEffect(abo); ModelModelWrapper aboSplitTEModel = transformationTreeExtensions.initializeTransformationTree( transformationTree.initializeTransformationTree(SCCtransformation.extractMapping(), "TriggerEffect", abo, "coreSCChart", aboSplitTE, "coreSCChart-splitTriggerEffect"); aboNormalized = SCCtransformation.transformSurfaceDepth(aboSplitTE); ModelWrapper aboNormalizedModel = transformationtransformationTree.addTransformationToTree(SCCtransformation.extractMapping(), aboSplitTEModel, "SurfaceDepth", aboSplitTE, aboNormalized, "normalizedCoreSCChart"); aboSCG = SCGtransformation.transformSCG(aboNormalized); ModelWrapper aboSCGModel = transformationTree.addTransformationToTree(SCGtransformation.extractMapping(), aboNormalizedModel, "SCC2SCG", "splitTriggerEffect", abo, "ABO", aboSplitTE, "ABO-splitTriEff"); tranformationTree = transformationTreeExtensions.root(aboSplitTEModel); |
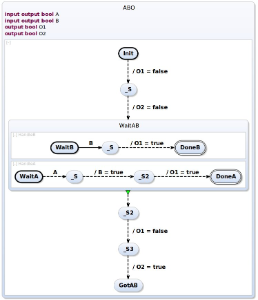
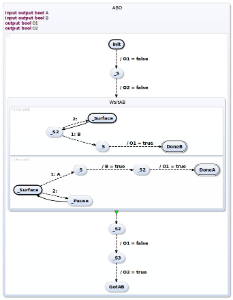
The result of transformation is the following SCChart. ABO-splitTriEff.
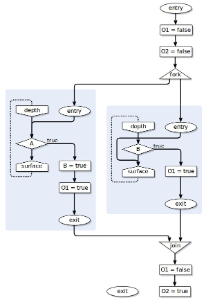
Resulting TransformationTree has following structure.
Furthermore the TransformationTree now contains the following mapping information.
...
aboNormalized, aboSCG,"SCG");
tree = transformationTree.root(aboSCGModel); |
The resulting TransformationTree has following structure and representing each step and model of the transformation.
Furthermore the TransformationTree now contains mapping information for the whole transformation chain.
Now we can use an additional feature of KTM, the resolving of mappings between arbitary models.
The following code has starts with an instance of the initial ABO SCChart and SCG, along with the TranformationTree above.
| Code Block | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||
@Inject
extension TransformationTreeExtensions
//Find nodes of model instances in tree
val aboSCCModelWrapper = transformationTree.findModel(aboSCC,"coreSCChart");
val aboSCGModelWrapper = transformationTree.findModel(aboSCG,"SCG");
//resolve
val mapping = resolvemapping(aboSCCModelWrapper, aboSCC, aboSCGModelWrapper, aboSCG); |
The returned mapping is a multi mapping between all object in aboSCC and their resulting objects in aboSCG.
This mapping can now displayed in models or used for various information propagation between elements of the models.
Also a more detailed view is available, showing all EObjects relation.
Visualisation
If you have a TransformationTree file (.ktmt) you can open a KLighD visualisation by right-clicking on file in project-tree and selecting 'Open Transformation Tree'.
Diagram Options
Model Visualisation: If enabled tries to visaulize selected models with KLighD else a EObject-represenation is created.
EObject Attributes: If enabled shows Attributes of EObject in EObject-represenation.
Selective mapping edges: If enabled shows only selected mapping edges.
Interaction
CTRL+CLICK: Selects a Node in TransformationTree as source and displays its represented model.
SHIFT+CLICK: Selects a Node in TransformationTree as target, displays both models and the resolved mapping as edges (currenly only between States/Regions).
If Selective selective mapping edge is enabled no mapping edges are displayed. If you select (CLICK) an element in one of the two model its relation to corresponding element is displayed. You can multi-select with CTRL+CLICK or deselect by clicking on an edge.