Responsible:
- Christoph Daniel Schulze
KLay Force is an implementation of the force-based layout approach where edges are regarded as springs pulling together the nodes they connect, while unconnected nodes are pushed apart from one another. The objective is to compute a state where this physical system reaches an equilibrium.
This page describes the available layout options as well as the general architecture of the algorithm.
Contents
Layout Options
ToDo
List available layout options.
Architecture
The architecture basically consists of two chunks: the graph model and the actual implementation of the algorithm.
Graph Model
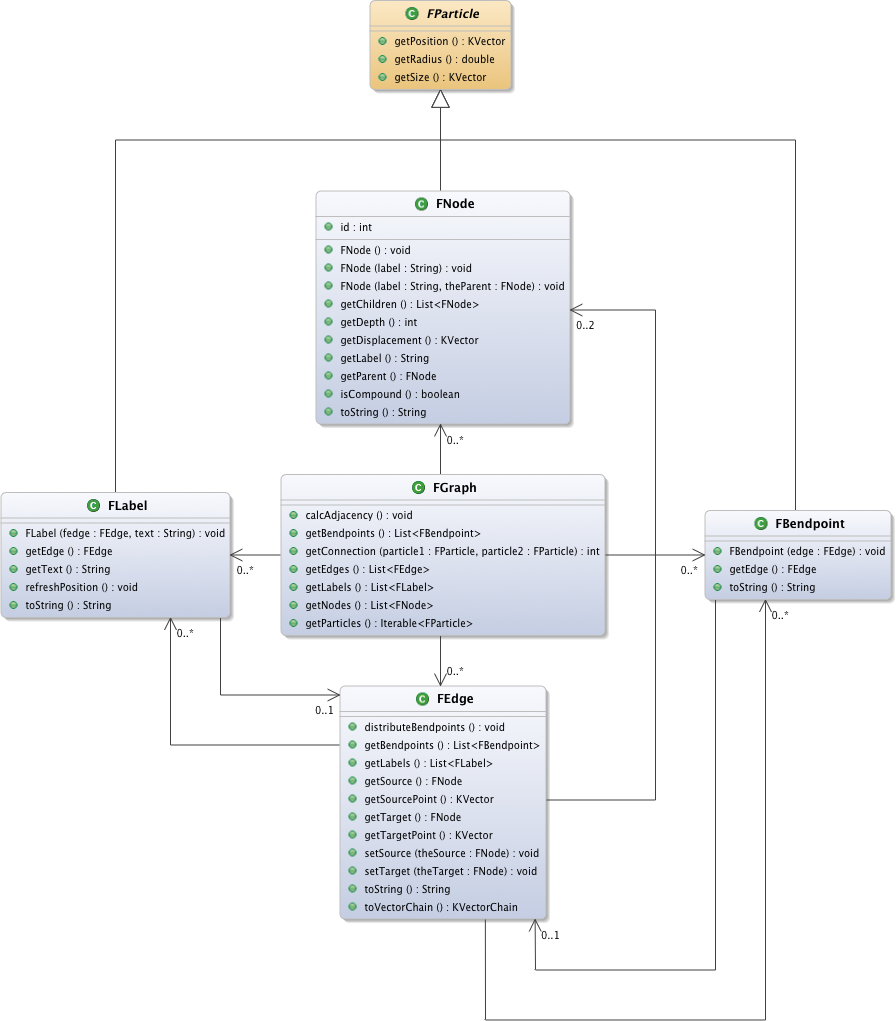
KLay Force uses a custom, lightweight graph model whose root is the FGraph class. FNode instances are connected through FEdge instances that, to be routed properly, can have FBendpoint instances. Edges and nodes can have a number of FLabel instances. Nodes, labels, and bend points are considered FParticles since they exert forces on each other. The following is a class diagram of the basic graph model:
Algorithm
ToDo
Describe architecture.