Comments
You can simply use JavaDoc-style comments to comment you SCChart. The comments will appear in the synthesized diagram as comment boxes. You can toggle these boxes in your sidebar.
Additionally, for documentation reason, you can annotate different elements to give them a user-defined style. E.g. colorize a state or comment box for visual effect. Use html-like color codes for different colors. Please read more on annotations in the section below.
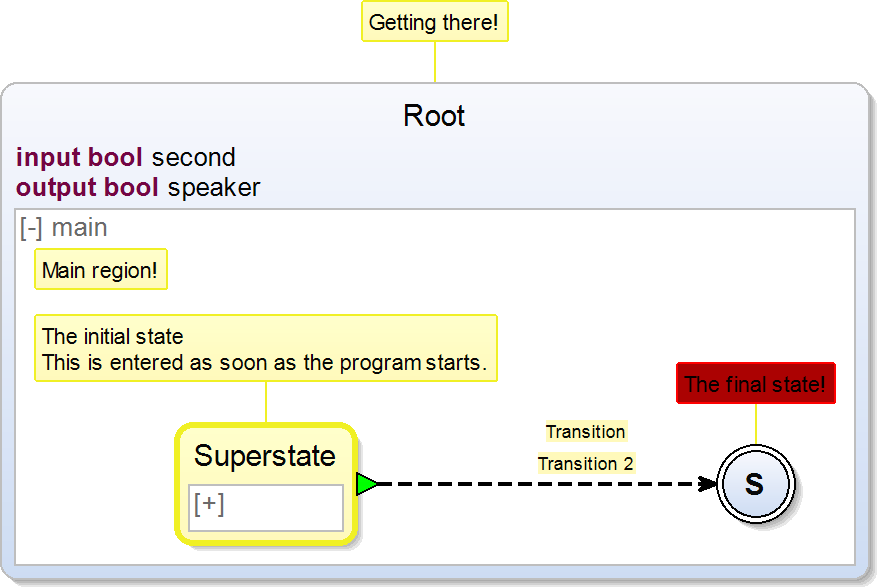
/**
* Getting there!
*/
scchart Root {
/** Test */
input bool second
output bool speaker
/**
* Main region!
*/
region main:
/**
* The initial state
* This is entered as soon as the program starts.
*/
@foreground f0f024
@background ffffcc
@backgroundTarget fff9ba
initial state Superstate {
initial state R1
}
/** Transition */
/** Transition 2 */
join to S
/**
* The final state!
* @foreground f00
* @background a00
*/
final state S
}
Tuples
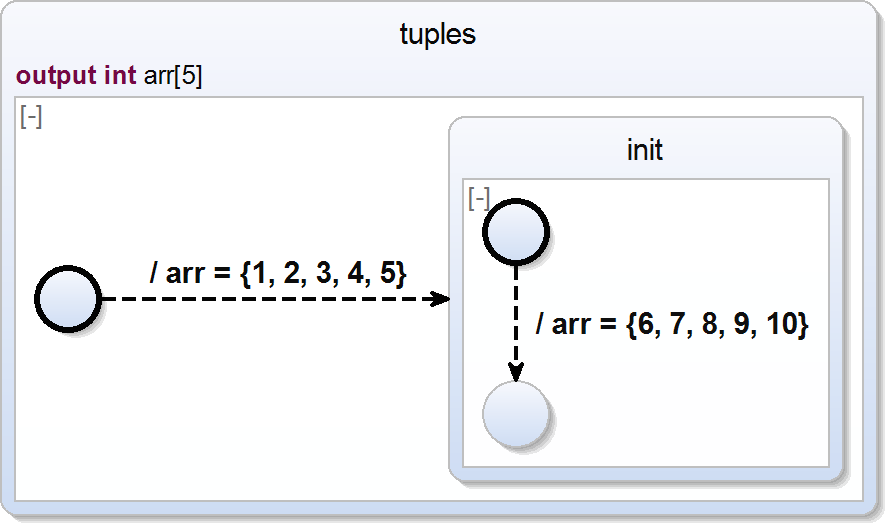
You can assign a whole vector at once to an array.
scchart tuples {
output int arr[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
initial state init {
entry do arr = {6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
}
}
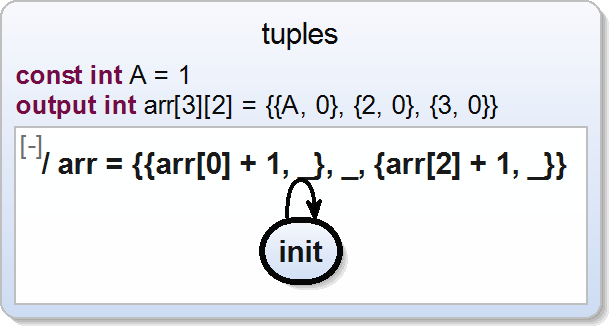
To assign only certain values of an array, you can also use the ignore value placeholder. Consult the expression manual for further information.
scchart tuples {
const int A = 1
output int arr[3][2] = {{A,0}, {2,0}, {3,0}}
initial state init
--> init do arr = {{arr[0] + 1, _}, _, {arr[2] + 1, _}}
}
This would, for example, result in c code assignments as displayed on the right.
void logic(TickData* d) {
d->_g0 = d->_GO;
if (d->_g0) {
d->arr[0][0] = 1;
d->arr[0][1] = 0;
d->arr[1][0] = 2;
d->arr[1][1] = 0;
d->arr[2][0] = 3;
d->arr[2][1] = 0;
}
d->_g2 = d->_pg1;
if (d->_g2) {
d->arr[0][0] = d->arr[0] + 1;
d->arr[2][0] = d->arr[2] + 1;
}
d->_g1 = d->_g0 || d->_g2;
}