KTM - KIELER Transformation Mapping
Topics
This subproject provides a tracing mechanism for arbitary model-elements across multiple model transformations, based on EMF.
The main propose of KTM is to allow bidirectional information transfer between abstract models and their resultant transformed models.
Transformation Tree Model
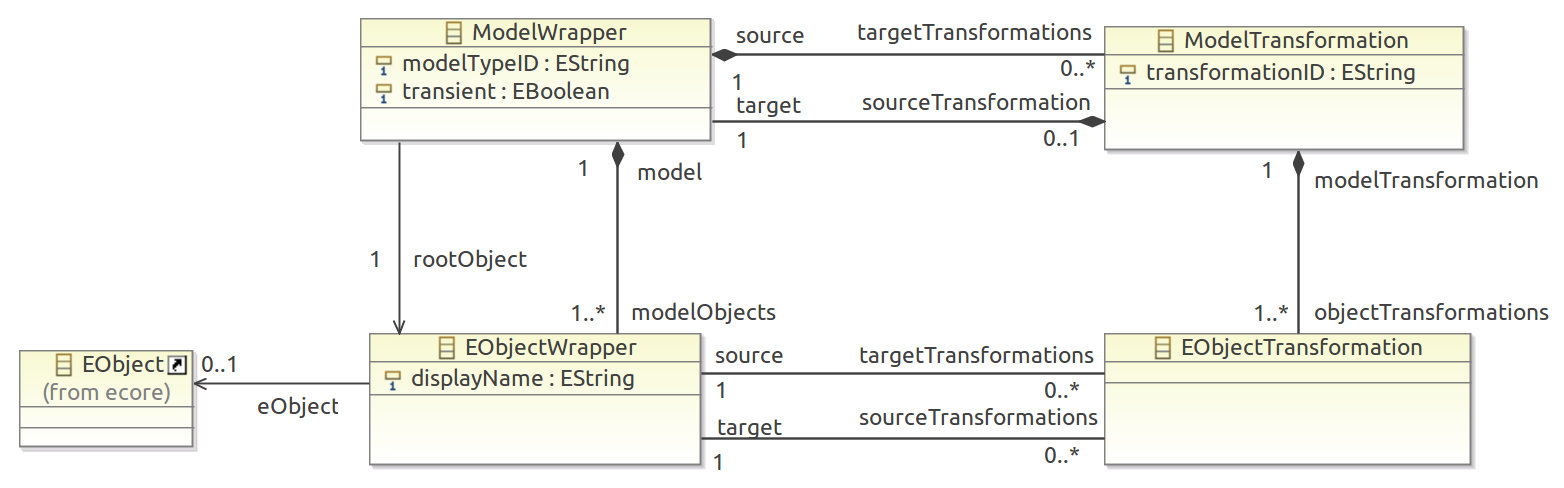
To offer a mapping between model-elements during multiple transformations KTM introduces a model called TransformationTree to represent these relations.
It is based on an EMF-Metamodel.
The structure of the model can be separated into two parts.
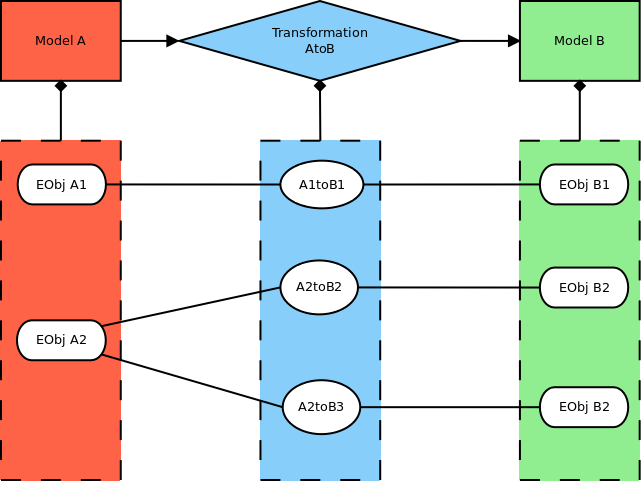
First part (upper half) is a tree of transformations. Each ModelWrapper-class is a representation of a model which is transformed. So ModelWrapper are nodes and ModelTransformations are edges. Thus the ModelWrapper representing the initial-source-model of all transformation is also the root of a TransformationTree-model.
Second part (lower half) is object-mapping. Instances of models contain EObjects as their elements, which are represented by EObjectWrapper-class in this metamodel. The EObjectWrapper of two models are connected with EObjectTransformations-class to express their origination relationship in corresponding model transformation.
An abstract example of an instance of this model:
Extensions
Two classes are provided by this project to extend functionality of the core model.
TransformationMapping (JavaDoc)
The main propose of this class is generation of a object-mapping during transformation process.
Therefor it provides different functions for incremental registering of single parent-child-relations between EObjects.
Furthermore, the extension allows to extract the mapping and check completeness of mapped elements against content of transformed models.
TransformationTreeExtensions (JavaDoc)
This class provides all functionalities to easily traverse and search in a TransformationTree.
Furthermore, it allows to modify trees by creating, deleting or appending new transformations and transformed models.
Additionally this extension provides functionality to extract a concrete mapping between two arbitary model intances from a TransformationTree.
Implementation Details
- All references to EObjects in EObjectWrapper are references to a copy of the original EObject. This allows to represent immutable mapping. To reidentify corresponding EObjects TransformationTreeExtensions provides search functions which will check for structural matching models.
- Models in TransformationTrees may be transient. This indicates that all references to EObjects in all Elements of the transient model are removed. Thus these models can't be source of a new appended transformation and can not be associated with it's original model. The main propose of this feature is to improve scalability of TransformationTrees by removing unnecessary references to internal model, but preserve traversing functionality of the object-mapping.
- Mappings can be incomplete causing resulting transfromation tree to be incomplete. A incomplete tree does not represent every object in a model with a corresponding Element. This may break some paths of element transformations, but allows to omit model-immanent objects like annotations from mapping. TranformationMapping extension provies a function to check completeness of mapping against its models.
Example
Creating Mapping during Transformation
The following code is a modifcation of the tranformation "Spilt Trigger and Effects" of SCCharts.
Create TransformationTree with Mapping
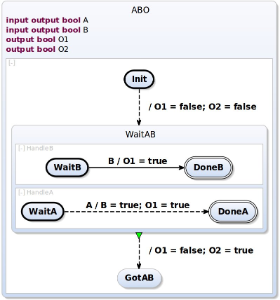
To test the transformation and mapping we will transform th following ABO-SCChart.
The following code snipped performs the transformation on our ABO-example, extracts the mapping and creates a transformation tree.
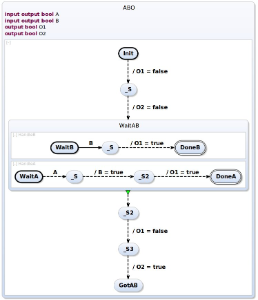
The result of transformation is the following SCChart. ABO-splitTriggerEffect.
Resulting TransformationTree has following structure.
Furthermore the TransformationTree now contains the following mapping information.
Here you can see the effect of the transformation causing the transformation to split up.