...
[1] R. von Hanxleden, B. Duderstadt, C. Motika, S. Smyth, M. Mendler, J. Aguado, S. Mercer, and O. O’Brien. SCCharts: Sequentially Constructive Statecharts for Safety-Critical Applications. In Proc. ACM SIGPLAN Conference on Programming Language Design and Implementation (PLDI’14), Edinburgh, UK, June 2014. (pdf)
ABRO Example
In the following we will describe the basic elements using the famous ABRO example:
...
- In the first line you see how an SCChart is defined using the scchart keyword where the ID of the SCChart will be ABRO. An optional label can be inserted after ABRO using "<LABEL>".
- In the next three lines variables are declared, namely, A, B, R and O, where O is initialized with the value false. A, B, and R are inputs which must not be initialized and get there valued from the environment.
- An SCChart typically contains concurrent regions which are introduced with the keyword region as shown in Line 6.
- Every region must at least have one state, and every region must exactly have one initial state. An initial state ABO is defined for region Main in Line 7.
- Every state is terminated by a ; as shown in line 11 for state HandleA.
- If you like to specify internal behavior of a state, you can add concurrent regions to a state in { <regions> } as done for state ABO or state WaitAB.
- Transitions outgoing from a state must be declared right before a state is terminated with ;. For example a transition from state WA to state DA is declared in Line 11.
- Transitions can have triggers and effects which are separated by a dash: <trigger>/<effects>. Multiple sequential effects are separated by a ;. The transition in Line 11 declares just a trigger A (a dash is not necessary in this case), while the transition from line 18 declares only an effect O = true (here the dash is mandatory).
- There are three types of transitions: 1. normal/weak abort transitions -->, 2. strong abort transitions o-> and 3. termination/join transitions >->.
Detailed SCT Syntax of SCCharts Elements
SCChart, Initial State, State, Transition and Immediate Transition
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
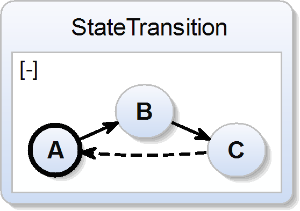
| scchart StateTransition {
initial state A
--> B;
state B
--> C;
state C
--> A immediate;
} |
|
| Column |
|---|
|
 |
Variable
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| scchart Variable {
int var1;
bool var2;
int var3 = 3;
bool var4 = false;
input int var5;
output float var6;
input output bool var7;
initial state A
--> B;
state B;
} |
|
| Column |
|---|
|
 |
Transition: Trigger & Effect
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| scchart TriggerEffect {
input int var1;
output bool var2;
initial state A
--> B with var1 == 3 / var2 = true;
state B;
} |
|
| Column |
|---|
|
 |
Super State
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
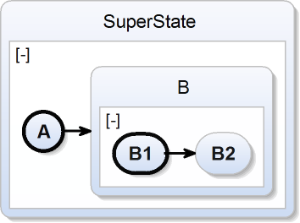
| scchart SuperState {
initial state A
--> B;
state B {
initial state B1
--> B2;
state B2;
};
} |
|
| Column |
|---|
|
 |
Super State: Final States & Termination Transition
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
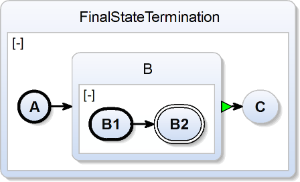
| scchart FinalStateTermination {
initial state A
--> B;
state B {
initial state B1
--> B2;
final state B2;
}
>-> C;
state C;
} |
|
| Column |
|---|
|
 |
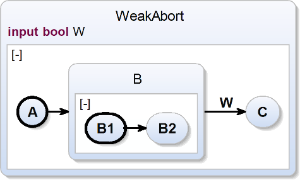
Super State: Weak Abort Transition
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| scchart WeakAbort {
input bool W;
initial state A
--> B;
state B {
initial state B1
--> B2;
state B2;
}
--> C with W;
state C;
} |
|
| Column |
|---|
|
 |
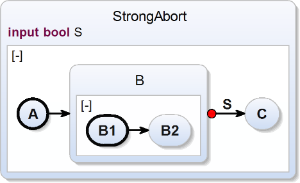
Super State: Strong Abort Transition
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| scchart StrongAbort {
input bool S;
initial state A
--> B;
state B {
initial state B1
--> B2;
state B2;
}
o-> C with S;
state C;
} |
|
| Column |
|---|
|
 |
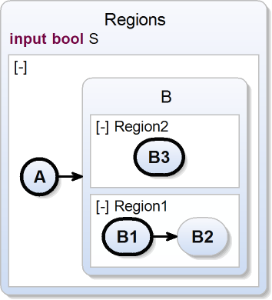
Concurrent Regions (inside a Super State)
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| scchart Regions {
input bool S;
initial state A
--> B;
state B {
region Region1 :
initial state B1
--> B2;
state B2; region Region2 :
initial state B3;
};
} |
|
| Column |
|---|
|
 |
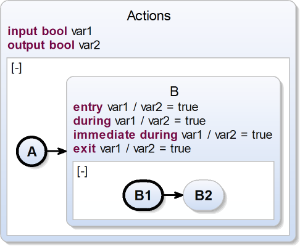
Entry Action, During Action, Exit Action
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| scchart Actions {
input bool var1;
output bool var2;
initial state A
--> B;
state B {
entry var1 / var2 = true;
during var1 / var2 = true;
immediate during var1 / var2 = true;
exit var1 / var2 = true;
initial state B1
--> B2;
state B2;
};
} |
|
| Column |
|---|
|
 |
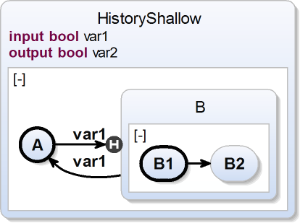
Shallow History Transition
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| scchart HistoryShallow {
input bool var1;
output bool var2;
initial state A
--> B shallow history with var1;
state B {
initial state B1
--> B2;
state B2;
}
--> A with var1;
} |
|
| Column |
|---|
|
 |
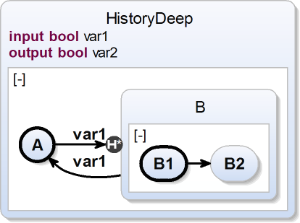
Deep History Transition
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| scchart HistoryDeep {
input bool var1;
output bool var2;
initial state A
--> B history with var1;
state B {
initial state B1
--> B2;
state B2;
}
--> A with var1;
} |
|
| Column |
|---|
|
 |
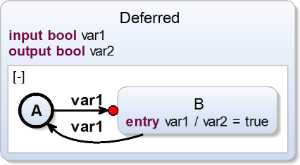
Deferred Transition
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| scchart Deferred {
input bool var1;
output bool var2;
initial state A
--> B deferred with var1;
state B {
entry var1 / var2 = true;
}
--> A with var1;
} |
|
| Column |
|---|
|
 |
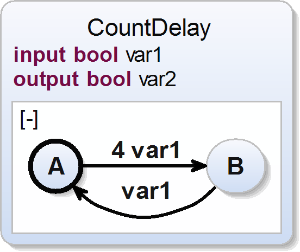
Transition with Count Delay
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| scchart CountDelay {
input bool var1;
output bool var2;
initial state A
--> B with 4 var1;
state B
--> A with var1;
} |
|
| Column |
|---|
|
 |
Array
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| scchart Array {
int myArray[10][2];
initial state init
--> done with myArray[1][0] == 1 / myArray[2][1] = 2;
final state done;
} |
|
| Column |
|---|
|
 |
Signal
| Column |
|---|
|
| Code Block |
|---|
| scchart Signal {
input signal i;
output signal o
initial state init
--> done with i / o;
final state done;
} |
|
...













