This is preliminary and incomplete documentation. You've been warned.
KLay Layered supports a whole bunch of layout options. Every single one of them is documented here.
Contents
Overview
For a general introduction on layout options, see the KIML documentation. KLay Layered supports layout options defined by KIML and defines additional custom layout options.
Supported KIML Layout Options
KLay Layered supports the following standard layout options defined by KIML. Note that the default value may be altered (highlighted yellow). These layout options are documented on KIML's Layout Options page.
| Option | ID | Type | Applies to | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alignment | de.cau.cs.kieler.alignment | Enum | Nodes | AUTOMATIC |
| Aspect Ratio | de.cau.cs.kieler.aspectRatio | Float | Parents | 1.6 |
| Border Spacing | de.cau.cs.kieler.borderSpacing | Float | Parents | 20 |
| Comment Box | de.cau.cs.kieler.commentBox | Boolean | Nodes | false |
| Debug Mode | de.cau.cs.kieler.debugMode | Boolean | Parents | false |
| Diagram Type | de.cau.cs.kieler.diagramType | String | ||
| Direction | de.cau.cs.kieler.direction | Enum | Parents | RIGHT |
| Edge Label Placement | de.cau.cs.kieler.edgeLabelPlacement | Enum | Labels | UNDEFINED |
| Edge Routing | de.cau.cs.kieler.edgeRouting | Enum | Parents | POLYLINE |
| Hypernode | de.cau.cs.kieler.hypernode | Boolean | Nodes | false |
| Label Side | de.cau.cs.kieler.labelSide | Enum | Parents | SMART |
| Label Spacing | de.cau.cs.kieler.labelSpacing | Float | Edges Nodes | -1.0 |
| Layout Hierarchy | de.cau.cs.kieler.layoutHierarchy | Boolean | Parents | false |
| Minimal Height | de.cau.cs.kieler.minHeight | Float | Nodes | 0.0 |
| Minimal Width | de.cau.cs.kieler.minWidth | Float | Nodes | 0.0 |
| No Layout | de.cau.cs.kieler.noLayout | Boolean | false | |
| Node Label Placement | de.cau.cs.kieler.nodeLabelPlacement | EnumSet | Nodes | |
| Port Constraints | de.cau.cs.kieler.portConstraints | Enum | Nodes | UNDEFINED |
| Port Label Placement | de.cau.cs.kieler.portLabelPlacement | Enum | Nodes | OUTSIDE |
| Port Offset | de.cau.cs.kieler.offset | Float | Ports | |
| Port Side | de.cau.cs.kieler.portSide | Enum | Ports | UNDEFINED |
| Priority | de.cau.cs.kieler.priority | Int | Edges Nodes | |
| Randomization Seed | de.cau.cs.kieler.randomSeed | Int | Parents | 1 |
| Separate Connected Components | de.cau.cs.kieler.separateConnComp | Boolean | Parents | true |
| Size Constraint | de.cau.cs.kieler.sizeConstraint | EnumSet | Nodes | |
| Size Options | de.cau.cs.kieler.sizeOptions | EnumSet | Nodes | DEFAULT_MINIMUM_SIZE |
| Spacing | de.cau.cs.kieler.spacing | Float | Parents | 20 |
Custom Layout Options
| Option | ID | Type | Applies to | Default | Dependency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crossing Minimization | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.crossMin | Enum | Parents | LAYER_SWEEP | |
| Cycle Breaking | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.cycleBreaking | Enum | Parents | GREEDY | |
| Edge Spacing Factor | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.edgeSpacingFactor | Float | Parents | 0.5 | |
| Edge Label Side Selection | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.edgeLabelSideSelection | Enum | Parents | SMART | |
| Feedback Edges | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.feedBackEdges | Boolean | Parents | false | |
| Fixed Alignment | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.fixedAlignment | Enum | Parents | NONE | nodePlace=BRANDES_KOEPF |
| Interactive Reference Point | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.interactiveReferencePoint | Enum | Parents | CENTER | |
| Layer Constraint | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.layerConstraint | Enum | Nodes | NONE | |
| Maximal Iterations | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.nodeLayering | Int | Parents | 10.000.000 | nodeLayering=NETWORK_SIMPLEX |
| Merge Edges | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.mergePorts | Boolean | Parents | false | |
| Merge Hierarchy-Crossing Edges | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.mergeHierarchyPorts | Boolean | Parents | true | layoutHierarchy=true |
| Node Layering | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.nodeLayering | Enum | Parents | NETWORK_SIMPLEX | |
| Node Placement | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.nodePlace | Enum | Parents | BRANDES_KOEPF | |
| Port Anchor Offset | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.portAnchor | Object | Ports | ||
| Thoroughness | de.cau.cs.kieler.klay.layered.thoroughness | Int | Parents | 7 |
The Most Important Options
TODO: Write a bit of documentation about the most important layout options and how to use them, possibly with a simple example or something.
Detailed Documentation
This section explains every layout option in more detail. See the KIML documentation for more information on KIML layout options. Those options are only mentioned here if KLay Layered adds some custom behavior.
Crossing Minimization
Crossing minimization determines the ordering of nodes in each layer, which influences the number of edge crossings. This option switches between one of several algorithms that can be used to minimize crossings. Possible values are:
- LAYER_SWEEP
The layer sweep algorithm iterates multiple times over the layers, trying to find node orderings that minimize the number of crossings. The algorithm uses randomization to increase the odds of finding a good result. To improve its results, consider increasing the Thoroughness option, which influences the number of iterations done. The Randomization seed also influences results. - INTERACTIVE
Orders the nodes of each layer by comparing their positions before the layout algorithm was started. The idea is that the relative order of nodes as it was before layout was applied is not changed. This of course requires valid positions for all nodes to have been set on the input graph before calling the layout algorithm. The interactive layer sweep algorithm uses the Interactive Reference Point option to determine which reference point of nodes are used to compare positions.
Cycle Breaking
KLay Layered tries to position nodes in a way that all edges point rightwards. This is not possible if the input graph has cycles. Such cycles have to be broken by reversing as few edges as possible. The reversed edges end up pointing leftwards in the resulting diagram. There are different cycle breaking algorithms available:
- GREEDY
This algorithm reverses edges greedily. The algorithm tries to avoid edges that have the Priority property set. - INTERACTIVE
The interactive algorithm tries to reverse edges that already pointed leftwards in the input graph. This requires node and port coordinates to have been set to sensible values.
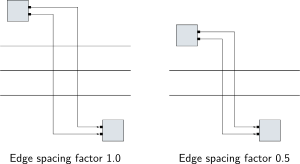
Edge Spacing Factor
The edge spacing factor determines the amount of space between edges, relative to the regular Spacing value. The idea is that we don't need as much space between edges as we do between nodes.
Edge Label Side Selection
Document!
Feedback Edges
Document!
Fixed Alignment
The BRANDES_KOEPF node placement algorithm computes several different node placements. One of the placements is chosen by the algorithm, usually the one that takes the least amount of space. With this option, a particular result can be chosen.
This option should usually be left alone.
Interactive Reference Point
Interactive layering, crossing minimization, and cycle breaking algorithms use node positions to sort nodes into layers or to determine the order of nodes in each layer. However, it is unclear if for example the top left corners of nodes should be compared, or the bottom left corners — different settings might lead to different results. The interactive reference point determines which part of nodes is used to compare their positions. It provides the following settings:
- TOP_LEFT
The top left corner of a node is taken as the reference point. - CENTER
The center of a node is taken as the reference point.
Layer Constraint
Document!
Maximal Iterations
Delimits the amount of depth-first-search iterations performed by the network simplex layering strategy. Large, highly connected graphs might require a long time to be processed. This property serves as a timeout after which an exception is raised.
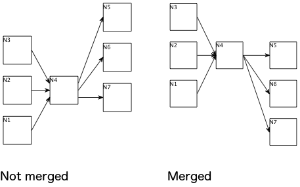
Merge Edges
In the KGraph model, edges can either connect to nodes through ports or directly. In the latter case, KLay Layered will introduce a virtual port for each edge, which results in all edges connecting to the node at different points in the final drawing. If this option is switched on, KLay Layered will only generate up to one input and one output port for each node. The option is set on a parent node and applies to all of its children, but not to the parent node itself.
Merge Hierarchy-Crossing Edges
Document!
Node Layering
Decides which algorithm is used to compute the layer each node is placed in. We have different algorithms available, with different optimization goals:
- NETWORK_SIMPLEX
This algorithm tries to minimize the length of edges. This is the most computationally intensive algorithm. The number of iterations after which it aborts if it hasn't found a result yet can be set with the Maximal Iterations option. - LONGEST_PATH
A very simple algorithm that distributes nodes along their longest path to a sink node. - INTERACTIVE
Distributes the nodes into layers by comparing their positions before the layout algorithm was started. The idea is that the relative horizontal order of nodes as it was before layout was applied is not changed. This of course requires valid positions for all nodes to have been set on the input graph before calling the layout algorithm. The interactive node layering algorithm uses the Interactive Reference Point option to determine which reference point of nodes are used to compare positions.
Node Placement
Document!
Port Anchor Offset
Document!
Thoroughness
There are heuristics in use all over KLay Layered whose results often improve with the number of iterations computed. The thoroughness is a measure for telling KLay Layered to compute more iterations to improve the quality of results, at the expense of performance.